Table of Contents
Indoor aquatic plants are a beautiful and functional addition to any home, providing both visual appeal and environmental benefits. Whether you’re an experienced aquarist or new to the world of indoor gardening, aquatic plants offer an opportunity to create a tranquil and natural atmosphere in your home. With the right selection and care, these plants can thrive indoors, creating lush underwater gardens or simply adding elegance to water features and aquariums.
In this guide, we will explore the different types of indoor aquatic plants, their benefits, how to care for them, and how to create your own aquatic garden. We will also delve into the many factors to consider when introducing these plants into your home environment.
What Are Indoor Aquatic Plants?
Indoor aquatic plants are species that thrive in water, either partially submerged or fully submerged. They play an essential role in aquatic ecosystems by oxygenating the water, providing shelter and food for aquatic life, and filtering out toxins. These plants come in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and colors, making them suitable for various types of indoor environments.
The Importance of Aquatic Plants
- Water Filtration: Aquatic plants are natural filters, absorbing nutrients from the water. They help prevent the buildup of excess nitrogen and other pollutants, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment for both plants and aquatic animals.
- Oxygen Production: Through the process of photosynthesis, aquatic plants produce oxygen, which is vital for the survival of fish and other organisms in an aquarium or pond. They also contribute to a healthier, more balanced ecosystem.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Beyond their ecological functions, aquatic plants bring visual appeal to your home. Their vibrant colors and graceful movement in the water provide a calming, zen-like atmosphere in any space.
Types of Indoor Aquatic Plants
When it comes to choosing indoor aquatic plants, it’s important to understand the different categories of these plants. Each category has different requirements and growth habits, so selecting the right type for your space is key to creating a thriving ecosystem.
Floating Plants
Floating plants float on the water’s surface and have their roots submerged below, hanging in the water. These plants require a steady supply of light and nutrients. Floating plants are often chosen for their ability to help prevent algae growth by blocking excess sunlight from reaching the water’s surface.
Examples of Floating Plants:
- Water Lettuce (Pistia stratiotes): This plant has rosette-shaped leaves that resemble lettuce and can grow in various water conditions. Water Lettuce helps absorb excess nutrients in the water and keeps the water clean.
- Duckweed (Lemna minor): Duckweed is a tiny, fast-growing plant that forms a thick carpet of green across the water’s surface. It is an excellent oxygenator and filter for water bodies.
Submerged Plants
Submerged plants are entirely submerged in water, and many of them are oxygenating plants. They are vital for oxygen production and serve as natural filters, making them an essential component of any indoor aquatic garden.
Examples of Submerged Plants:
- Anacharis (Egeria densa): Anacharis is a popular submerged plant that grows quickly and helps oxygenate water. It is ideal for aquariums and smaller water features.
- Hornwort (Ceratophyllum demersum): Hornwort is a hardy, floating plant that can be planted in substrates or left to float freely in the water. It is known for its fast growth and ability to absorb excess nutrients from the water.
Marginal Plants
Marginal plants grow around the edges of ponds or water features, where they may have their roots submerged but their leaves exposed to the air. These plants are ideal for shallow water and can be placed in aquariums, bowls, or terrariums.
Examples of Marginal Plants:
- Arrowhead (Sagittaria spp.): Arrowhead is an easy-to-grow plant that thrives in shallow water and can add a vertical element to your indoor aquatic garden. It is particularly effective in smaller aquariums.
- Water Iris (Iris pseudacorus): Water Iris is a striking aquatic plant with vibrant yellow flowers and tall, sword-like leaves. It grows best in shallow water and is perfect for larger aquatic displays.

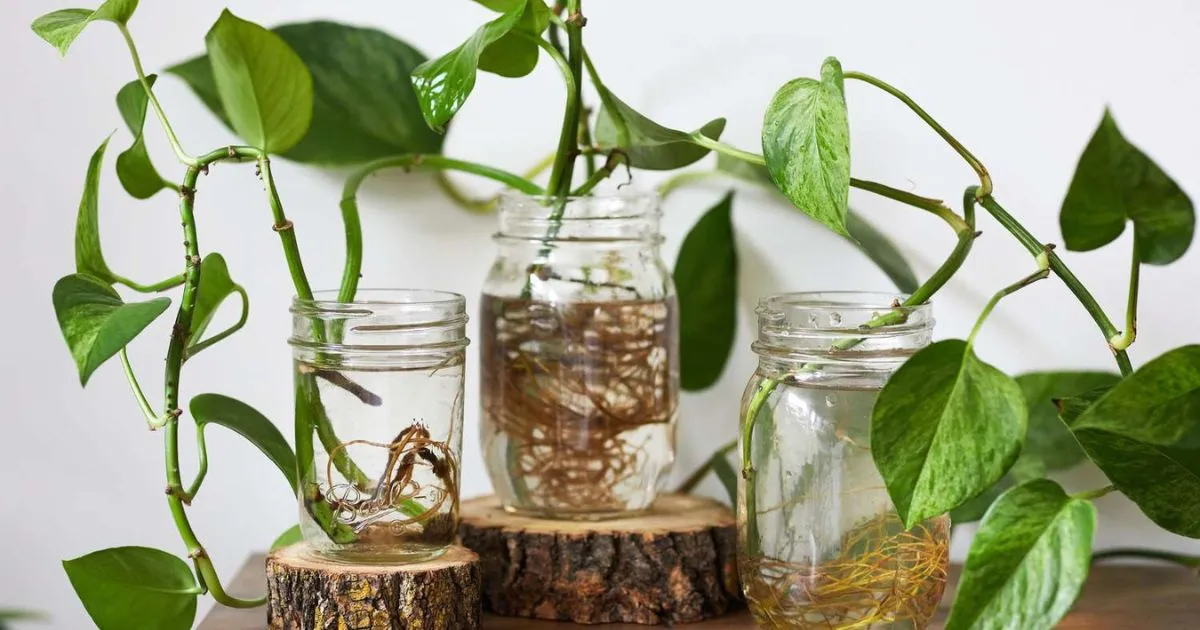
Key Benefits of Indoor Aquatic Plants
Indoor aquatic plants offer a range of benefits, from improving air quality to enhancing the aesthetic appeal of your home. Here’s why you should consider adding them to your living space:
1. Natural Filtration and Water Purification
Aquatic plants absorb excess nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium from the water. In an aquarium or pond, they help to break down waste materials and improve water quality by preventing the accumulation of harmful substances. In this way, they provide natural filtration without the need for mechanical filters.
2. Enhancing Indoor Humidity
Aquatic plants release moisture into the air through a process known as transpiration. This natural process increases the humidity in your home, which can help alleviate dry skin, respiratory issues, and prevent damage to wood furniture and flooring caused by low humidity.
3. Aesthetic Appeal and Tranquil Ambiance
Having indoor aquatic plants adds a calming element to any space. Their vibrant green colors, soothing movement in the water, and delicate flowers create a peaceful atmosphere. The gentle motion of the plants floating or swaying in the water can help create a sense of tranquility, ideal for reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
4. Low Maintenance
Most indoor aquatic plants are relatively low-maintenance. Unlike traditional houseplants, which require frequent watering, pruning, and repotting, aquatic plants are naturally adapted to thrive in their water-filled environment. Once their setup is properly established, they can largely take care of themselves.
How to Care for Indoor Aquatic Plants
Caring for indoor aquatic plants requires some attention to detail, but with proper care, these plants can thrive for years. Here are some tips on how to ensure your aquatic plants remain healthy and vibrant:
1. Choosing the Right Container
The first step to caring for aquatic plants is selecting the right container. Whether you’re using an aquarium, a decorative bowl, or a dedicated aquatic garden, the container should have enough space for the plants to grow. Ensure that the container provides adequate depth and surface area for the plants and allows for good water circulation.
2. Providing Adequate Light
Aquatic plants require different levels of light depending on their species. Some plants, like Anacharis, thrive in low light conditions, while others, such as Water Lettuce, need bright, direct light. Consider placing your aquatic plants near a window or investing in an aquarium light to provide the appropriate lighting conditions.
3. Maintaining Water Quality
Regular water changes are essential for keeping your aquatic plants healthy. The water should be kept clean and free from toxins. Ensure the temperature, pH, and hardness of the water match the requirements of your plants. Water parameters can be tested using simple test kits to maintain a balanced and healthy environment for your plants and any aquatic life that may inhabit the space.
4. Fertilizing Aquatic Plants
Most indoor aquatic plants benefit from occasional fertilization, especially in a closed environment like an aquarium. You can use liquid fertilizers that are specially formulated for aquatic plants or organic fertilizers designed for pond plants. Be cautious not to over-fertilize, as this can lead to algae growth and an imbalance in water quality.
5. Pruning and Maintenance
Pruning is important for keeping your aquatic plants healthy and preventing them from overcrowding the space. Trim any dead or yellowing leaves to encourage new growth and ensure that the plants don’t become too overgrown. Regularly remove any floating debris or fallen leaves to keep the water clean.
Designing Your Indoor Aquatic Garden
Creating an indoor aquatic garden is a fun and rewarding project. Here are some tips on how to design and set up your own aquatic garden:
1. Select the Right Plants
Start by selecting a variety of plants that suit the space you are working with. Consider mixing submerged plants, floating plants, and marginal plants to create visual interest. Be sure to choose plants that have similar light and water requirements to ensure compatibility.
2. Choose the Right Location
Consider the lighting conditions in the area where you plan to place your aquatic garden. If you don’t have access to natural light, you may need to install a grow light to provide your plants with the light they need. Also, ensure the container is placed in a safe spot away from drafts and high-traffic areas.
3. Add Decorative Elements
Enhance the beauty of your aquatic garden with rocks, driftwood, or ornamental aquatic decorations. These elements can add texture and depth to your water feature, making it more visually appealing and inviting.
Conclusion
Indoor aquatic plants bring a unique combination of beauty, tranquility, and ecological benefits to your home. Whether you choose to create a serene aquatic garden, an aquarium, or a simple decorative water feature, these plants help to purify the air, maintain a balanced water ecosystem, and enhance the overall aesthetic of your living space.
With the right care and attention, indoor aquatic plants can thrive for years, offering both visual and environmental benefits. Experiment with different types of aquatic plants, experiment with lighting and positioning, and enjoy the soothing ambiance that these plants can provide.
FAQ: Common Questions About Indoor Aquatic Plants
1. How do I prevent algae growth in my indoor aquatic garden?
Algae growth can be controlled by limiting excess nutrients and ensuring proper water circulation. Floating plants like Water Lettuce and Duckweed can help block excess light and absorb nutrients that algae need to thrive. Regular water changes and proper plant maintenance also help prevent algae overgrowth.
2. Can I keep aquatic plants in a container without fish?
Yes, you can keep aquatic plants in a container without fish. Many aquatic plants will thrive on their own as long as they have adequate light, water quality, and nutrients. However, adding fish can help create a balanced ecosystem and promote natural plant growth.
3. How often should I change the water in my aquatic garden?
The frequency of water changes depends on the size of the container and the number of plants. In general, performing water changes every two weeks helps maintain water quality. For larger setups with more plants and fish, more frequent changes may be necessary.
4. What are the best beginner-friendly aquatic plants?
Beginner-friendly aquatic plants include Java Fern (Microsorum pteropus), Anubias (Anubias spp.), and Amazon Sword (Echinodorus spp.). These plants are hardy, low-maintenance, and adaptable to various water conditions, making them ideal for those new to indoor aquatic gardening.

